|
|
|
Industrial pollution |
Power generation |
Building demolition |
Air pollution is indication of disturbances to the composition of compounds in the atmosphere, as it may be summarized as shown:
- Excess emission of gases/vapors into atmosphere.
- Saturation of chemical compounds/particulates.
- Rate of dissipation < (smaller than) rate of absorption through various cycles (i.e. carbon and nitrogen cycle).
- Emergence of new chemical reactions of reactive and non-biodegradable compounds.
Global warming, acid rain, smog, ozone depletion are some effects of air pollution.
|
|
|
Cement factory pollution |
Car pollution |
Tar heating |
In relation to this, we may observe the cycle which involves in our daily lives: carbon and nitrogen cycle. These 2 cycles are the most important of all, regulating the composition of carbon and nitrogen of Earth.
Sources and Methods
We can classify major sources that lead to air pollution to the following categories:
- motor vehicle exhaust
- heat and power generation facilities
- industrial processes
- auto manufacturing
- fertilizers plants
- building demolition
- solid waste disposal
- solvent evaporation
- volcanic eruption
- fuel production
- roadway construction
- electrical components manufacturing
- extraction of metals
- forest fires
- agriculture.
Air Pollution Effects on Humans
- Pollution causes not only physical disabilities but also psychological and behavioral disorders in people.
- Reduced lung functioning.
- Irritation of eyes, nose, mouth and throat.
- Asthma attacks.
- Respiratory symptoms such as coughing and wheezing.

Air Pollution
- Increased respiratory disease such as bronchitis
- Reduced energy levels
- Headaches and dizziness
- Disruption of endocrine, reproductive and immune systems
- Neurobehavioral disorders
- Cardiovascular problems
- Cancer
- Premature death.
Effects of Air Pollution on Animals
- Acid rain (formed in the air) destroys fish life in lakes and streams.
- Excessive ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun through the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere which is eroded by some air pollutants, may cause skin cancer in wildlife.
- Ozone in the lower atmosphere may damage lung tissues of animals.
Air Pollution Effects on Trees and Plants
Trees Damaged by Acid Rain
- Acid rain can kill trees, destroy the leaves of plants, can infiltrate soil by making it unsuitable for purposes of nutrition and habitation.
- Ozone holes in the upper atmosphere can allow excessive ultraviolet radiation from the sun to enter the Earth causing damage to trees and plants.
- Ozone in the lower atmosphere can prevent plant respiration by blocking stomata (openings in leaves) and negatively affecting plants’ photosynthesis rates which will stunt plant growth; ozone can also decay plant cells directly by entering stomata
Air Pollutants
Gaseous Air Pollutants
Main types of gaseous air pollutants:
- Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
- Oxides of nitrogen (NOx = NO + NO2)
- Ozone (O3)
Sulfur dioxide and nitric oxide (NO) are the primary air pollutants, and ozone is a secondary pollutant (though there are negligible direct emissions of the gas itself).
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is both a primary and secondary air pollutant.
Other important gaseous pollutants are: ammonia, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
Sources of SO2
- Energy Production
- Electric power generation
- Petroleum refining
- Other combustion
- Commercial and residential use
- Combustion for industry use
- Production processes
- Extraction and distribution of fossil fuels
- Transport
- Road transport
- Other Transport (such as aviation, ships, trains).
Fuel itself can produce some nitrogen (for example, oil and coal contain around 0.5 – 1.5% of nitrogen, and natural gas contains less than that , most of nitrogen oxides' production comes from the reaction of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen within the combustion chamber.
Nitrogen Oxides
- The two main nitrogen oxides are nitric oxide (NO), or nitrogen monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) the sum of which is equal to NOx.
- Nitric oxide (NO) is a colorless gas. Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is a gas of reddish-brown color with a distinct sharp, biting odor.
Sources
- Combustion of fuels always produces both NO2 and NO. But almost 90% of the NOX combustion product is in the form of NO which is then oxidized to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in the air. Therefore, only a small percentage of NO2 found in the atmosphere is directly emitted there in this form. The rest has been formed as a result of chemical reactions in the atmosphere itself.
- Road transport contributed nearly half of all nitrogen emissions, followed by contributions from electric power generating plants which only contributed around 20% of total nitrogen emissions.
- Road transport
- Other Transport
3. Energy Production
- Electric power generation
- Petroleum refining
- Other combustion
4. Combustion for industry use
5. Production processes
6. Extraction and distribution of fossil fuels.
Natural Sources of Nitrogen Oxide Emissions
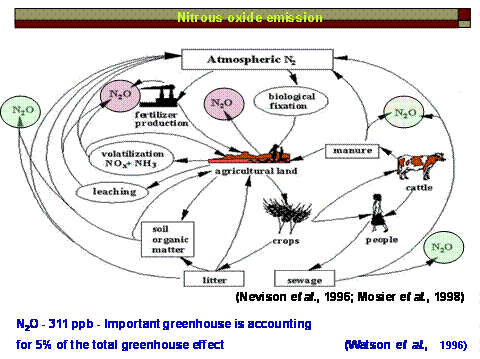
Nitric oxide (NO) is also emitted by soils
Sources of Ammonia Emissions
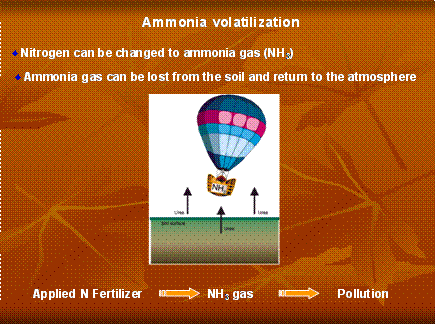
Agriculture is by far the biggest source of ammonia emissions. Livestock farming and animal waste account for the biggest percentage of total ammonia emissions which are due to the decomposition of urea from large animal wastes and uric acid from poultry wastes.
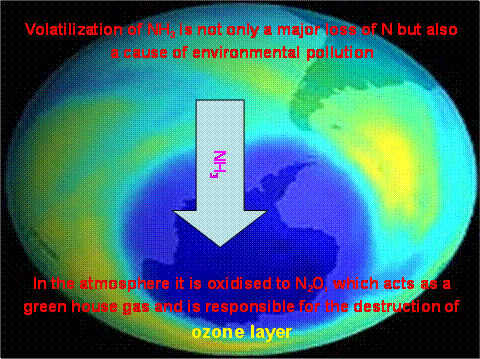
Major sources:
- Livestock – contributes more than 50% of all emissions
- Fertilizer application
- Oceans
- Vegetation
- Biomass burning
Carbon monoxide (CO)
- The combustion of carbon-based fuels produces carbon dioxide (CO2).
- But not all such combustion is complete, and this leads to the production of carbon monoxide (CO).
- Motor vehicles and industry are among the largest anthropogenic sources of carbon monoxide emissions.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are defined as organic compounds which easily evaporate and enter the atmosphere. VOCs may include a wide range of organic air pollutants, from pure hydrocarbons to partially oxidized hydrocarbons to organic compounds containing chlorine, sulfur, or nitrogen.
Major sources:
- Painting (evaporation of solvents)
- Oil production (flaring and venting of gas)
- Oil refining (flaring and fugitive emissions)
- Distribution of oil or refinery products (evaporation from storage, displacement losses when venting tanks)
- Dry cleaning (final drying of clothes)
- Production of alcoholic drinks (breweries and distilleries)
- Arable farming (crop growing, silage manufacture, sludge spreading)
Natural Sources of Volatile Organic Compounds
Forests are the primary natural sources of VOC emissions. Tropical forests are estimated to produce about half of all global natural non-methane VOC emissions. Plants synthesize many organic molecules and release some VOCs (including a range of terpenes) into the atmosphere.
Ozone (O3)
Ozone can be found in:
- The stratosphere, one of the upper layers of the atmosphere, where it occurs naturally,
- The troposphere, the lowest layer of the atmosphere, where it occurs both naturally and as a result of human-generated emissions.
- The natural stratospheric ozone is considered to be of beneficial nature – it keeps harmful excessive ultraviolet sunlight from reaching the surface of the Earth.
- Ozone which is formed in the troposphere as a result of anthropogenic emissions of primary pollutants, has negative effects on humans and the natural environment. And from this point of view it is an air pollutant.
- This human-caused ozone in the troposphere is a secondary pollutant because it is produced by the reaction of primary pollutants, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons [including VOCs], in the presence of sunlight.
- The tropospheric ozone is the main component of the photochemical smog.
Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- Persistent organic pollutants are compounds which are resistant to degradation and persistent in the environment, with half lives of years in the soil or sediment and days in the atmosphere.
- Such compounds may include dioxins, furans, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides such as DDT.
- They enter the food chains via the process of biomagnifications accumulated in human and animal tissue, and are capable of long range transport through being attached to airborne particles.
Sources of Persistent Organic Pollutants:
Some POPs are used as pesticides. Others are used in industrial processes as well as in the production of goods such as solvents, polyvinyl chloride and medicines.
Air Pollution Management
In the field of advancing technology, improvisation of current method in the treatment and control of pollutants in industrial areas, prevention of greater degree of pollution and proper management of waste in hand with economical cost. Also in mind the practice of sustainable development with the implementation of environmental technology to give a greater benefit to every individuals. By classifications, research and development is divided into:
Alternative Technologies
- Offering various possibilities to the current method in treatment and control of pollution
- Current alternatives in applications:
- Soil vapor extraction
- Bioventing
- Biopiles
- Land farming
- Low temperature thermal desorption
- Air sparging
- Biosparging
- Natural attenuation
- In situ ground water bioremediation
- Dual-phase extraction
- Desalination of sea water
- many scientists think that the next step of generating nuclear energy is by fission of atoms
Clean Technologies
- Renewable sources which can be used many times, involves minimal cost and also restricted use of hazardous materials in use, especially in the use of energy
- Current clean technologies available:
- Hydropower
- Solar energy
- Wind power
- Geothermal energy
- Biomass energy
- Tillage
- Vegetation
- Compost
Creative/Innovative Technologies
- New class of invention which could lead to greater efficiency in prevention of pollutions, or current improvement to a more refine technology
- Current creative/innovative technologies are:
- Sorbents
- Air cleaning
- In situ oxidation
- In situ well aeration
- Solvent extraction
- In situ flushing
- Solidification
- Soil washing
- Biological agents
- Dispersing agents
- Energy chips
- Cooling towers
Air Pollution Control
Wind Power
- Harness from wind generator in which maximum power can't be any greater than the kinetic energy of the air which passes through it per unit time
- Kinetic energy harness is directly proportional to (speed)3
- Expected actual power output would be a percentage of this, depending on the speed of the air after it has passed through the generator and on such factors as friction, radius of blade of the wind generator and density of air
Wind power generation
 
Water Fuel Cell
- Water as the source of energy which is separated into hydrogen and oxygen by a high voltage, high frequency electromagnetic field generated from a card of 12V battery
- Exhaust gases are a mixture of air and water vapor that is released back to atmosphere, eventually falling as rain
- Used in fuel cards, trucks, buses, aircraft, ships and power stations as well as any other equipment that uses coal, oil or gas as their current energy source
|
School bus with compressed natural gas as its fuel

School bus with compressed natural gas as its fuel
Catalytic Converters
- Installed in automobiles and various types of filters and scrubbers in industrial plants
- Exhaust gas transferred through small beads coated with metal that promote reactions neutralizing hazardous gases to harmless ones
Transportation Alternatives
Car pooling
Sharing of vehicles between individuals for transportation to work, as adopted by Malaysian Government to reduce vehicle traffic on road and also reduce the emission of exhaust gases (i.e. carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), oxides of nitrogen (NOx), lead (Pb) and sulphur dioxide (SO2)
Public transport
Promote the use of public transport for example underground rail or monorail which is fast, efficient and environmental friendly, produce minimal emissions of greenhouse gases

Bye cycle is an alternative
Maintenance of Machineries and Vehicles
- Regular check ups and replacements of parts to ensure smooth and efficient use of the machineries and transportation
- Ensure the performance of machineries and transportation to meet the standard requirement, so as not to produce any hazardous material to be emitted to the environment
Simple Way to Control of Air Pollution
(a) By separating pollutions from harmless gases
(b) By converting pollutants to innocuous products before their release atmosphere. Techniques now-a-days applied is using cyclone collectors or electrostatic precipitators.
(c) Switching from coal to gas fuel.
(d) Growing plants capable of fixing CO, (Phaseolus vulgaris, Daucus carota, Coleus blumli etc.) NO and other gaseous pollutions (Vitis, Pinus, Junipers, Quercus, Pyrus, Ribes)
http://www.studentsguide.in/biology/pollution-environment/control-of-air-pollution.html



